In modern cultivation, creating a consistent environment is fundamental. Agricultural plastic films, including those we produce at HGDN, are engineered polymer sheets designed to modify and control growing conditions. Their function moves beyond simple covering; they are active components in managing microclimates. As a dedicated greenhouse film supplier, we approach these products through the lens of material science, and here we explain the operational principles behind them.
The Core Function: Modifying the Radiant Energy Balance
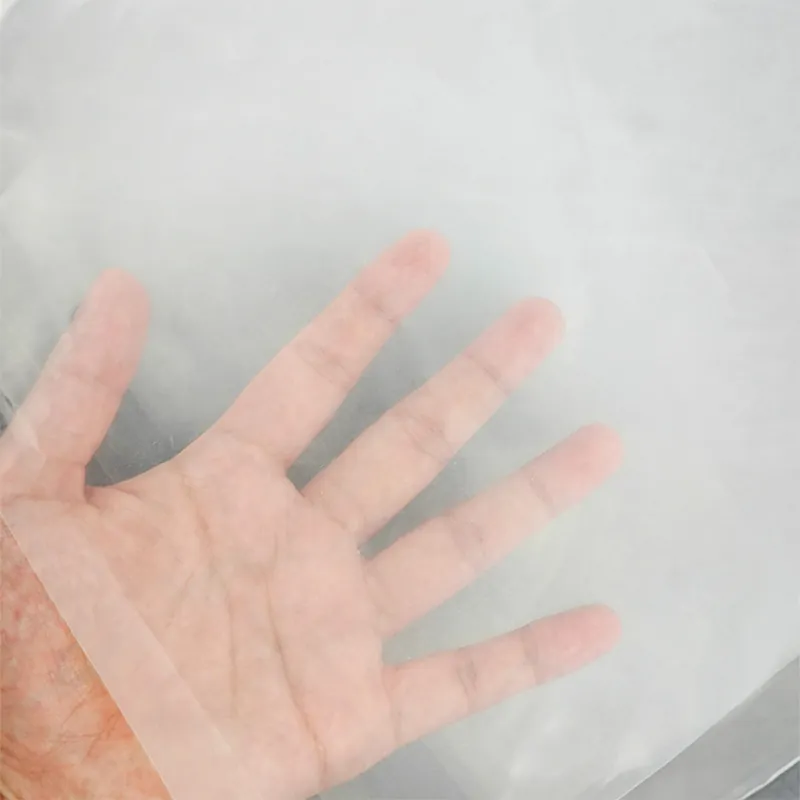
These films work primarily by interacting with solar radiation. A key metric is light transmission—the percentage of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) that passes through the material. Our films are engineered for high clarity to promote plant growth. Simultaneously, they filter or block specific wavelengths. For instance, many films contain additives to diffuse light, reducing shadows and encouraging uniform plant development. Another critical function is infrared (IR) management. Specialized layers within the film trap heat radiating from the soil at night, mitigating temperature drops. This balance between optical transparency and thermal regulation is a primary technical achievement of professional agricultural film manufacturers.
Material Construction and Protective Mechanisms
The performance and longevity of a film are dictated by its polymer chemistry and physical structure. We utilize metallocene-based resins and multi-layer co-extrusion, which allows us to embed different functionalities into distinct layers. One layer may contain UV stabilizers that absorb harmful radiation, preventing polymer chain breakdown and extending service life. Another layer can have an anti-drip formulation, causing condensation to spread into a thin film instead of forming droplets. This protects plants from water stress and disease. A third focus is mechanical strength, providing resistance to environmental stresses like wind or hail. This layered approach is what separates advanced films from basic coverings.
Integration and Application Across Systems
The utility of these films is realized through integration into broader agricultural systems. In greenhouse settings, the film is the primary cladding, working in concert with ventilation and irrigation systems to maintain precise parameters. In field applications, films are used as mulch, directly suppressing weeds and conserving soil moisture around plants. Their role also extends to propagation areas. For example, a clear film can be used to create a humid microclimate over a nursery tray, aiding in consistent seedling germination. This versatility makes a reliable greenhouse film supplier a partner in multiple stages of production, from seedling in a nursery tray to full-scale harvest.
Agricultural plastic films function as selective environmental filters. They manage light quantity and quality, influence thermal dynamics, and provide physical protection through sophisticated polymer engineering. Their effectiveness is a result of deliberate design in material composition and layered construction. For agricultural film manufacturers like us at HGDN, the objective is to provide films that deliver predictable, science-backed performance. From securing a greenhouse structure to supporting the early growth in a nursery tray, these films are integral tools for controlled, efficient cultivation.